LAHORE SPINE CARE
Neuro & Spine Care
Short Summary Diabetes can lead to a particular kind of nerve damage called diabetic neuropathy. All over the body, nerve damage can result from high blood sugar, or glucose. Most typically, diabetic neuropathy causes damage to the nerves in the feet and legs. Diabetic neuropathy symptoms might include numbness and pain in the hands, foot, and legs, depending on the damaged nerves. In addition, issues with the heart, blood vessels, urinary tract, and digestive system may result from it. A small number of persons get modest symptoms. However, some people may have severe discomfort and disability from diabetic neuropathy. About 50% of individuals with diabetes may experience diabetic neuropathy, a dangerous side effect of the disease. With steady blood sugar control and a healthy lifestyle, however, you can frequently avoid diabetic neuropathy or at least halt its progression.
Diabetic neuropathy is classified into four primary categories. One type of neuropathy or more types may be present in you.
-
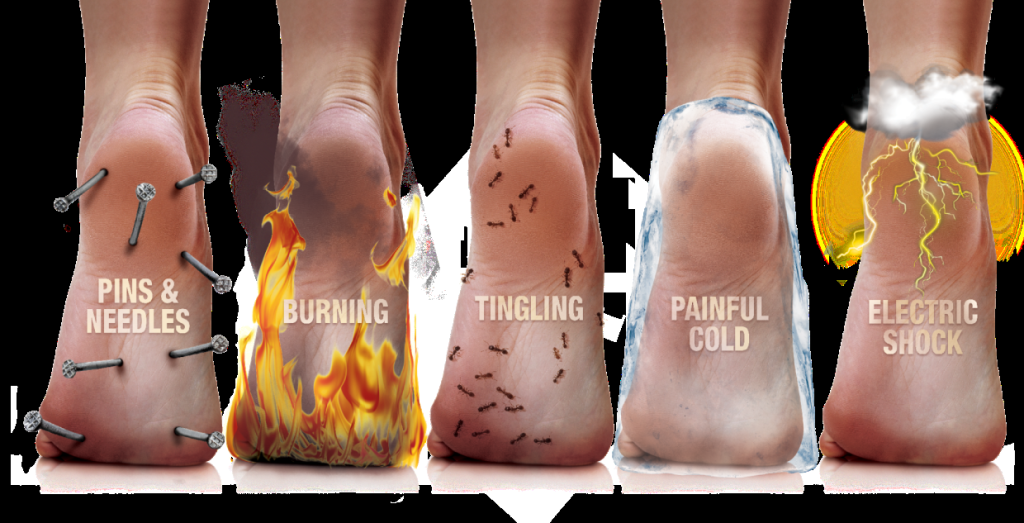
- Peripheral neuropathy Another name for this kind of neuropathy is distal symmetric peripheral neuropathy. This variety of diabetic neuropathy is the most prevalent. The hands and arms are affected after the feet and legs. Peripheral neuropathy symptoms and signs can include the following, which are frequently worse at night:
-
- numbness, diminished pain perception, or changes in body temperature
-
- Burning or tingling sensation
-
- cramping or sharp pains
-
- weakened muscles
-
- extreme sensitivity to touch; in certain cases, the weight of a bedsheet might cause agony
-
- Severe foot issues, including bone and joint degeneration, infections, and ulcers.
-
- severe thigh, hip, or buttock discomfort
-
- slender and weak thigh muscles
-
- Having trouble getting up from a sitting posture
-
- Pain in the chest or abdomen wall
-
- Double vision or trouble focusing
-
- One side of the face paralyzed
-
- Hand or finger numbness or tingling
-
- Hand weakness that could cause one to drop objects
-
- Soreness in the foot or leg
-
- Inadequacy resulting in trouble elevating the forefoot (foot drop)
-
- discomfort at the front of the leg
-
- a lack of knowledge of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia unawareness)
-
- blood pressure drops that might result in lightheadedness or fainting on getting up from a seated or lying down (orthostatic hypotension)
-
- bowel or bladder issues
-
- Gastro-pteresis, or slow stomach emptying, can result in nausea, vomiting, a full feeling in the abdomen, and appetite loss.
-
- Having trouble swallowing
-
- adjustments made by the eyes when they go from light to dark or from distance to near
-
- Sweating more or less
-
- issues relating to sexual responsiveness, such as erectile dysfunction in males and dry vagina in women
Diabetic neuropathy can affect anyone. But the following risk factors increase the likelihood of nerve damage:
-
- inadequate management of blood sugar. All complications related to diabetes, including damage to nerves, are more likely in those with uncontrolled blood sugar.
-
- history of diabetes. Long-term diabetes patients are more likely to develop diabetic neuropathy, particularly if their blood sugar is poorly managed.
-
- renal illness. Kidney damage can result from diabetes. Toxins released into the bloodstream by damaged kidneys can cause nerve injury.
-
- having a weight problem. The likelihood of developing diabetic neuropathy may rise in those with a body mass index (BMI) of 25 or higher.
-
- smoking. Smoking causes the arteries to constrict and harden, which lowers blood flow to the feet and legs. This affects the peripheral nerves and hinders the healing of wounds.
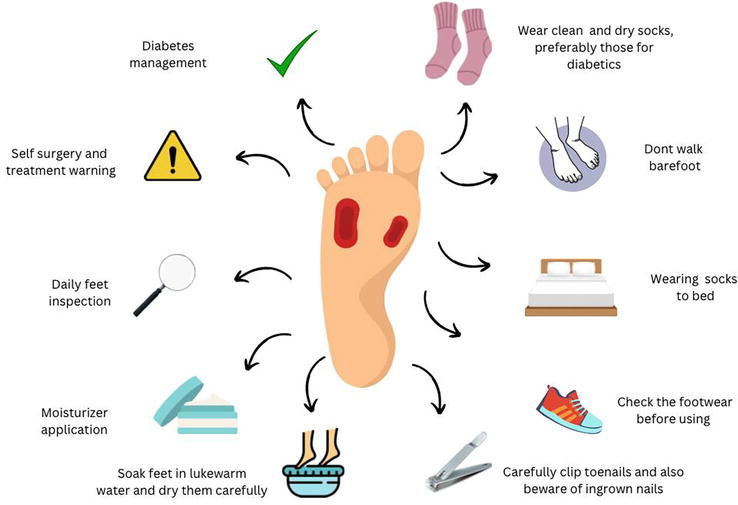
-
- Serious problems resulting from diabetic neuropathy include:
-
- hypoglycemia ignorance. If blood sugar is below 70 mg/dL, or 3.9 mmol/L (millimoles per liter), it typically results in dizziness, perspiration, and rapid heartbeat. However, autonomic neuropathy patients could not exhibit these symptoms.
-
- loss of a foot, leg, or toe. Because nerve injury can result in a loss of feeling in the foot, small cuts run the risk of developing into unseen sores or ulcers. Severe infections may cause tissue death or an infection that spreads to the bone. It can be necessary to amputate a toe, foot, or even a portion of the leg.
-
- urinary incontinence and urinary tract infections. If there is damage to the nerves controlling the bladder, the bladder.
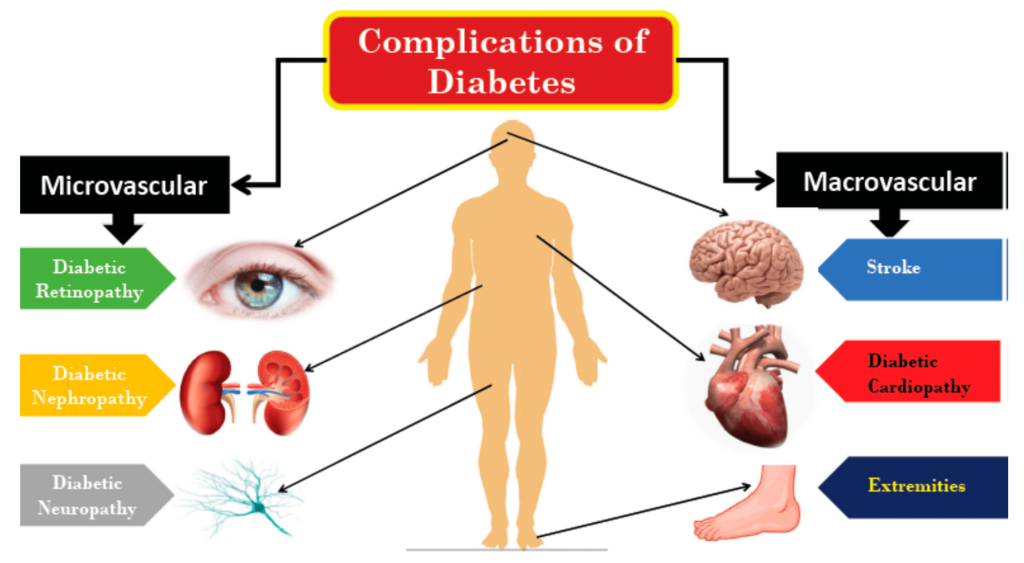
-
- Blood sugar control
-
- Pain management with medications
-
- Physical therapy
-
- Occupational therapy
-
- Alternative therapies such as acupuncture and massage
-
- Managing underlying factors such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol
-
- Improving circulation and reducing pain
-
- Increasing mobility and range of motion
-
- Strengthening muscles and improving balance
-
- Enhancing nerve conduction and sensation
-
- Promoting wound healing and preventing ulcers
-
- Improving overall quality of life
 Physiotherapy techniques
Physiotherapy techniques-
- Exercise programs (aerobic, strengthening, flexibility)
-
- Manual therapy (massage, joint mobilization)
-
- Electrical stimulation (TENS, NMES)
-
- Heat and cold therapy
-
- Foot care and orthotics
-
- Balance and coordination training
-
- Education on proper footwear and foot care
-
- Aquatic therapy
-
- Physical activity counseling
-
- Reduced pain and discomfort
-
- Improved mobility and function
-
- Enhanced quality of life
-
- Prevention of complications (ulcers, amputations)
-
- Improved blood sugar control
-
- Reduced risk of falls
-
- Improved overall health and well-being

Playlist
2 Videos
Physiotherapy consultation in Lahore.
0:16