LAHORE SPINE CARE
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Relationship Between Stress and Muscle Tightness: What You Need to Know
In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become an almost ubiquitous part of life. From deadlines at work to balancing family responsibilities, many of us feel the pressure in our daily lives. But did you know that stress can manifest physically, particularly through muscle tightness? Understanding the relationship between stress and muscle tightness can be crucial for both mental and physical well-being. Let’s dive into this connection and explore practical strategies to alleviate the discomfort.

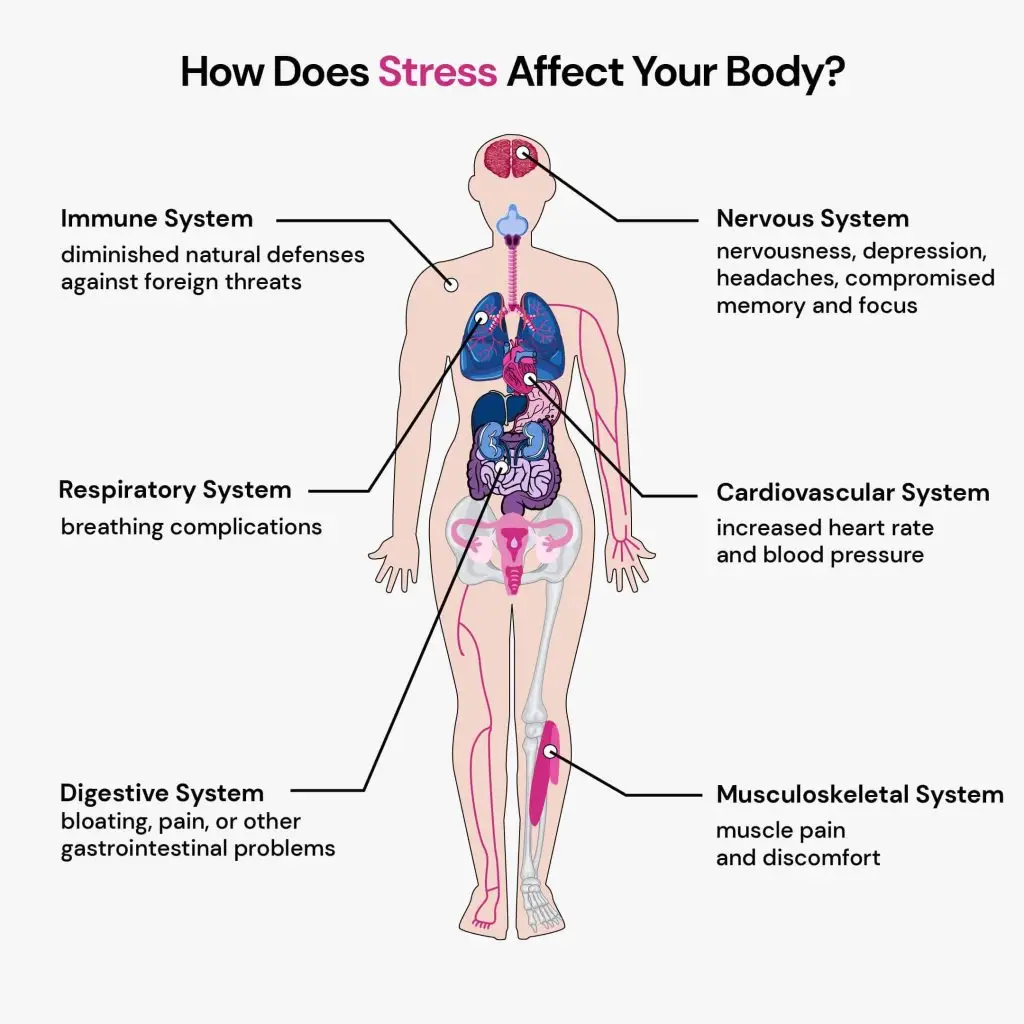
How Stress Affects the Body
Stress triggers a cascade of physiological responses designed to prepare your body for a perceived threat, commonly known as the “fight or flight” response. This involves the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which increase heart rate, elevate blood pressure, and redirect blood flow to essential areas like the muscles.
While this response can be beneficial in short bursts, chronic stress keeps the body in a state of heightened alertness, leading to various health issues. One of the more common physical manifestations of chronic stress is muscle tightness.
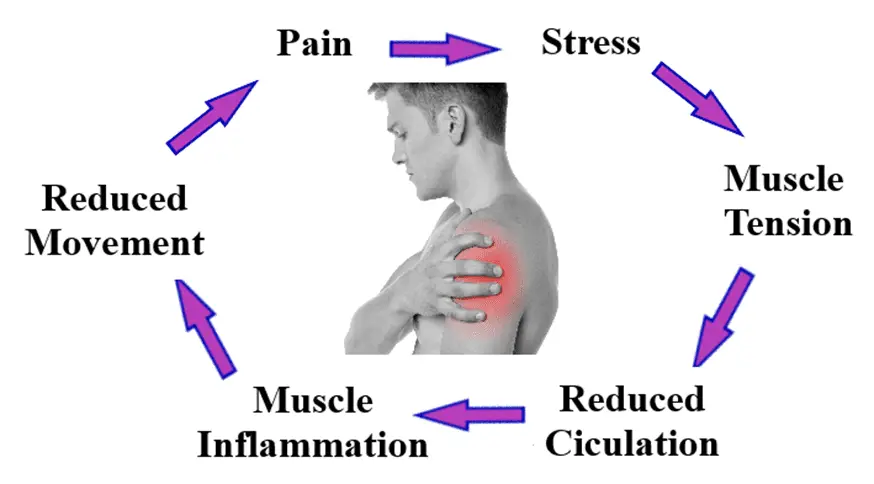
The Link Between Stress and Muscle Tightness
When you’re stressed, your body tenses up as a natural protective response. Here’s a closer look at how this happens:
- Muscle Contraction: Stress hormones cause muscles to contract in preparation for quick action. In the short term, this might make sense, but when stress becomes chronic, the muscles can remain in a contracted state for extended periods, leading to persistent tightness.
- Postural Changes: Stress can alter your posture, often causing you to hunch over or adopt other less-than-ideal postures. This can exacerbate muscle tension, particularly in the neck, shoulders, and back.
- Breathing Patterns: Stress often leads to shallow and rapid breathing, which can decrease oxygen flow to your muscles and contribute to tightness. Proper breathing is essential for muscle relaxation and overall well-being.
Common Areas Affected by Muscle Tightness
Muscle tightness due to stress commonly affects several areas of the body, including:
- Neck and Shoulders: These areas often bear the brunt of stress-related tension, leading to stiffness and discomfort. Prolonged tension here can contribute to headaches and reduced mobility.
- Back: Stress-induced tightness in the back can lead to chronic pain and discomfort, impacting your overall posture and mobility.
- Jaw: Stress can lead to clenching of the jaw or grinding of teeth, causing tightness in the jaw muscles and potentially leading to temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders.
Strategies for Managing Muscle Tightness
Understanding the link between stress and muscle tightness is the first step. Here are some effective strategies to manage and alleviate the discomfort:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity is a powerful stress reliever. It helps to release endorphins, which are natural mood lifters, and can also alleviate muscle tension. Activities like yoga, swimming, and walking are particularly effective.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices such as deep breathing, meditation, and progressive muscle relaxation can help manage stress and reduce muscle tightness. These techniques promote relaxation and can counteract the effects of stress on your body.
- Proper Posture: Being mindful of your posture, especially when sitting for long periods, can reduce muscle tension. Ergonomic adjustments to your workspace can also help maintain proper alignment and reduce strain.
- Stretching and Massage: Regular stretching can help relieve tight muscles and improve flexibility. Additionally, massage therapy can target specific areas of tension, providing relief and promoting relaxation.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and ensuring adequate sleep are all crucial for managing stress and preventing muscle tightness.
When to Seek Professional Help
While many strategies can be managed at home, persistent or severe muscle tightness may require professional intervention. If you experience chronic pain or significant discomfort, consider consulting with a healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist, chiropractor, or mental health specialist. They can provide tailored guidance and treatment options based on your individual needs.
Conclusion
The relationship between stress and muscle tightness is a significant factor in overall health and well-being. By understanding this connection and implementing effective strategies for stress management and muscle relaxation, you can mitigate the physical impact of stress and improve your quality of life. Remember, addressing stress is not only about managing your mind but also about caring for your body. Taking proactive steps can lead to a more balanced, healthy, and comfortable life.
LAHORE SPINE CARE is proudly powered by WordPress